Abstract
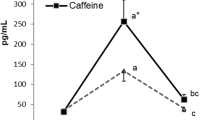
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) response was studied during two ultra endurance events—one laboratory 24 h protocol (9 men) with exercise intensity set to 60% of VO2max and one Adventure Race over 6 days (12 men/6 women) with a self-selected race pace, including rests, of about 38% of VO2max. In the 24-h protocol IL-6 level was elevated from 0.76 ± 0.48 pg mL−1 at rest to 7.16 ± 2.70 pg mL−1 at 6 h, and increased further to 10.58 ± 1.04 pg mL−1 at 12 h, but remained thereafter unchanged at 24 h, (10.89 ± 0.36 pg mL−1). All participants had nearly identical values at 12 and 24 h, supporting intensity as main determinant in the IL-6 response during prolonged exercise since exercise duration did not increase IL-6 level after 12 h. Possible confounding factors do not seem to influence the IL-6 concentration during the longer races (>12 h), but might very well do so during shorter exercise bouts. In the 6-day race IL-6 increased from rest to 24 h, but thereafter there was no change in plasma IL-6 value until the end of the race (mean 143.5 h). There was no elevation of TNF-α in any of the protocols, suggesting that the competitors were free from systemic inflammation. We conclude that during endurance exercise lasting >12 h intensity, and not duration, is the main determinant of the IL-6 response, while during shorter exercise bouts both intensity and duration contribute to the accumulation of IL-6 in plasma.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åstrand PO, Rodahl K (1986) Textbook of work physiology: physiological bases of exercise. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Singapore
Borg G (1962) Physical performance and perceived exertion. Studia Psychologica et Paedagogica, Series altera, Investigationes XI. Gleerup, Lund, pp 1–63
Brenner IK, Natale VM, Vasiliou P, Moldoveanu AI, Shek PN, Shephard RJ (1999) Impact of three different types of exercise on components of the inflammatory response. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 80:452–460
Cox AJ, Pyne DB, Cox GR, Callister R, Gleeson M (2008) Pre-exercise carbohydrate status influences carbohydrate-mediated attenuation of post-exercise cytokine responses. Int J Sports Med 29:1003–1009
Edwards KM, Burns VE, Ring C, Carroll D (2006) Individual differences in the interleukin-6 response to maximal and submaximal exercise tasks. J Sports Sci 24:855–862
Enqvist JK, Mattsson CM, Johansson PH, Brink-Elfegoun T, Bakkman L, Ekblom B (2010) Energy turnover during 24-hours and 6 days of adventure racing. J Sports Sci 28:947–955
Fernström M, Bakkman L, Tonkonogi M, Shabalina IG, Rozhdestvetskaya Z, Mattsson CM, Enqvist J, Ekblom B, Sahlin K (2007) Reduced efficiency, but increased fat oxidation in mitochondria from human skeletal muscle after 24 hours ultra-endurance exercise. J Appl Physiol 102:1844–1849
Fischer CP (2006) Interleukin-6 in acute exercise and training: what is the biological relevance? Exerc Immunol Rev 12:6–33
Fischer CP, Hiscock N, Basu S, Vessby B, Kallner A, Sjöberg LB, Febbraio MA, Pedersen BK (2004) Supplemetation with Vitamin-C and E inhibits the release of interleukin-6 from contraction human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 558:33–645
Gleeson M (2000) Interleukins and exercise. J Physiol 529:1
Gleeson M (2007) Immune function in sport and exercise. J Appl Physiol 103:693–699
Gleeson M, Bishop NC (2000) Special feature for the Olympics: effects of exercise on the immune system: modification of the immune response to exercise by carbohydrate, glutamine and anti-oxidant supplements. Immunol Cell Biol 78:554–561
Haack M, Sanchez E, Mullington JM (2007) Elevated inflammatory markers in response to prolonged sleep restriction are associated with increased pain experience in healthy volunteers. Sleep 30:1145–1152
Hiscock N, Fischer CP, Sacchetti M, van Hall MA, Pedersen BK (2005) Recombinant human interleukin-6 infusion during low intensity exercise does not enhance whole body lipolysis or fat oxidation in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 289:2–7
Keller C, Steensberg A, Pilegaard H, Osada T, Saltin B, Pedersen BK, Neufer PD (2001) Transcriptional activation of the IL-6 gene in human contracting skeletal muscle: influence of muscle glycogen content. FASEB J 15:2748–2750
Lindmark E, Diderholm E, Wallentin L, Siegbahn A (2001) Relationship between interleukin 6 and mortality in patients with unstabile coronary artery disease. Effect of an early invasive or non-invasive strategy. J Am Med Assoc 286:2107–2113
Lucas SJ, Anglem N, Roberts WS, Anson JG, Palmer CD, Walker RJ, Cook CJ, Cotter JD (2008) Intensity and physiological strain of competitive ultra-endurance exercise in humans. J Sports Sci 26:477–489
Mattsson CM, Enqvist JK, Brink-Elfegoun T, Johansson PH, Bakkman L, Ekblom B (2010) Reversed drift in heart rate but increased oxygen uptake at fixed work rate during 24 hours ultra-endurance exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 20:298–304
Nehlsen-Cannarella SL, Fagoaga OR, Nieman DC, Henson DA, Butterworth DE, Schmitt RL, Bailey EM, Warren BJ, Utter A, Davis JM (1997) Carbohydrate and the cytokine response to 2.5 h of running. J Appl Physiol 82:1662–1667
Nieman DC, Henson DA, McAnulty SR, McAnulty L, Swick NA, Utter AC, Vinci DM, Opiela SJ, Morrow JD (2002) Influence of vitamin C supplementation on oxidative and immune changes after an ultramarathon. J Appl Physiol 92:1970–1977
Nieman DC, Dumke CL, Henson DA, McAnulty SR, McAnulty LS, Lind RH, Morrow JD (2003) Immune and oxidative during and following the Western States Endurance Run. Int J Sports Med 24:541–547
Nieman DC, Dumke CL, Henson DA, McAnulty SR, Gross SJ, Lind RH (2005) Muscle damage is linked to cytokine changes following a 160 km race. Brain Behav Immun 19:398–403
Nieman DC, Bishop NC (2006) Nutrition strategies to counter stress to the immune system in athletes, with special reference to football. J Sports Sci 24:763–772
Northoff H, Berg A (1991) Immunologic mediators as parameters of the reaction to strenuous exercise. Int J Sports Med 1:9–15
Ostrowski K, Hermann C, Bangash A, Schjerling P, Nielsen JN, Pedersen BK (1998) A trauma-like elevation of plasma cytokines in humans in response to treadmill running. J Physiol 513:889–894
Ostrowski K, Rohde T, Asp S, Schjerling P, Pedersen BK (1999) Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine balance in strenuous exercise in humans. J Physiol 515:287–291
Ostrowski K, Schjerling P, Pedersen BK (2000) Physical activity and plasma interleukin-6 in humans—effect of intensity of exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 83:512–515
Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA (2008) Muscle an endocrine organ: focus on muscle-derived interleukin-6. Physiol Rev 88:1379–1406
Petersen BK, Hoffman-Goertz L (2000) Exercise and the immune system: regulation, integration and adaptation. Physiol Rev 80:1055–1081
Robson P (2003) Elucidating the unexplained underperformance syndrome in endurance athletes: the interleukin-6 hypothesis. Sports Med 33:771–781
Robson-Ansley PJ, de Milander L, Collins M, Noakes TD (2004) Acute interleukin-6 administration impairs athletic performance in healthy, trained male runners. Can J Appl Physiol 29:411–418
Robson-Ansley P, Barwood M, Canavan J, Hack S, Eglin C, Davey S, Hewitt J, Hull J, Ansley L (2009) The effect of repeated endurance exercise on IL-6 and sIL-6R and their relationship with sensations of fatigue at rest. Cytokine 45:111–116
Sprenger H, Jacobs C, Nain M, Gressner AM, Prinz H, Wesemann W, Gemsa D (1992) Enhanced release of cytokines, interleukin-2 receptors and neoptin after long-distance running. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 63:188–195
Steensberg A, van Hall G, Osada T, Sacchetti M, Saltin B, Klarlund Pedersen B (2000) Production of interleukin-6 in contracting human skeletal muscles can account for the exercise-induced increase in plasma interleukin-6. J Physiol 529:237–242
Suzuki K, Namaji S, Yamada M, Totsuka M, Sato K, Sugawara K (2002) Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise. Cytokine kinetics Exerc Immunol Rev 8:6–48
Suzuki K, Namaji S, Yamada M, Liu Q, Kurakake S, Okamura N, Kumae T, Umeda T, Sugawara K (2003) Impact of a competitive marathon race on systematic cytokine and neutrophil responses. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:348–355
Suzuki K, Peake J, Nosaka K, Okutsu M, Abbiss CR, Suriano R, Bishop D, Quod MJ, Lee H, Martin DT, Laursen PB (2006) Changes in markers of muscle damage, inflammation and HSP70 after an Ironman Triathlon race. Eur J Appl Physiol 98:525–534
Taylor HL, Buskirk E, Henschel A (1955) Maximal oxygen intake as an objective measure of cardio-respiratory performance. J Appl Physiol 8:73–80
Ullum H, Haahr PM, Diamant M, Palmo J, Halkjaer-Kristensen J, Pederson BK (1994) Bicycle exercise enhances plasma IL-6, but does not change IL-1, alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, or TNF-alpha pre-mRNA in BMNC. J Appl Physiol 77:93–97
van Hall G, Steensberg A, Sacchetti M, Fischer C, Keller C, Schjerling P, Hiscock N, Møller K, Saltin B, Febbraio MA, Pedersen BK (2003) Interleukin-6 stimulates lipolysis and fat oxidation in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3005–3010
Vgontzas AN, Zoumakis E, Bixler EO, Lin HM, Follett H, Kales A, Chrousos GP (2004) Adverse effects of modest sleep restriction on sleepiness, performance, and inflammatory cytokines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2119–2126
Vollmer-Conna U, Fazou C, Cameron B, Li H, Brennan C, Luck L, Davenport T, Wakefield D, Hickie I, Lloyd A (2004) Production of pro-inflammatory cytokines correlates with the symptoms of acute sickness behaviour in humans. Psychol Med 34:1289–1297
Zimberg IZ, Crispim CA, Juzwiak CR, Antunes HK, Edwards B, Waterhouse J, Tufik S, de Mello MT (2008) Nutritional intake during a simulated adventure race. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 18:152–168
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge with sincere gratitude the courageous efforts of our subjects. They also thank their supportive colleagues at Åstrand Laboratory of Work Physiology. The study was financially supported by grants from The Swedish National Centre for Research in Sports and the Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by William Kraemer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallberg, L., Mikael Mattsson, C., Enqvist, J.K. et al. Plasma IL-6 concentration during ultra-endurance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 111, 1081–1088 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1737-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1737-7